In the United States, gerrymandering is the term that refers to the definition of electoral districts in order to favor a particular group or political party. This impacts the results of the elections and the representation of certain communities, like Latinos and African Americans, among others, according to the Brennan Center for Justice, ally organization of Factchequeado.
This issue becomes more pressing whenever the House of Representatives changes, given the fact that their members represent the electoral districts. The members of the House of Representatives are renewed every two years. The next elections are on November 5th, on the same day of presidential elections. *
Lee esta historia en español haciendo clic aquí.
Next, we’ll explain the process of gerrymandering, how it affects voters and how the Supreme Court of Justice positioned itself regarding the accusations that this process is ill-intentioned.
How does the process work?
After each population census, which happens approximately every 10 years, the seats at the House of Representatives (50 in total, one corresponding to each state) are redistributed. This process is defined as reapportionment and it is based on each state’s population.
After this step is done, each state can redefine the limits of their electoral district (this is known as redistricting). This is because each of the 435 members of the House of Representatives represents an electoral district.
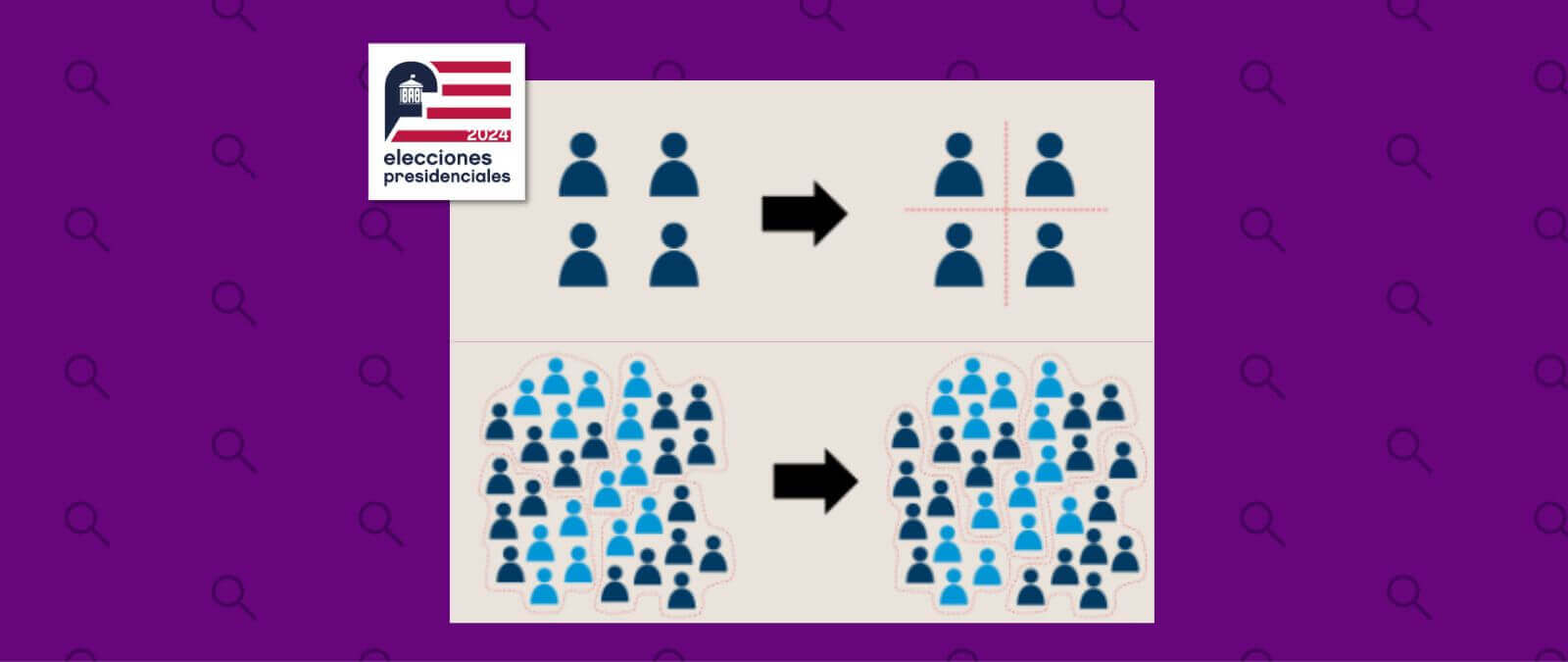
We call it gerrymandering when the redistricting process is done with the intention of favoring a particular group or political party.
The term references the governor of Massachusetts Elbridge Gerry, who, during his administration at the beginning of the 19th century, redefined a district and the form in the map resembled a salamander. A caricature published in the Boston Gazette showed the district drawn as a satirical animal, called the “Gerry-mander,” which gave birth to a term used now popularly, as explained by the British Encyclopedia.
How does it affect voters?
Theoretically, redistricting processes should be based only on demographic changes, so that the House of Representatives accurately reflects the state that chose it.
However, as explained by PolitiFact, ally organization of Factchequeado, “state legislators can use the redistricting process to group voters in districts where they can maximize favorable results for the majoritarian party.” Additionally, they explain that “instead of establishing a relatively even mixture of voters in each district, there’s a tendency to creating either strongly conservative or strongly liberal districts.”
Gerrymandering is normally done by two techniques: cracking and packing.
In the former, “there is a grouping of people with similar characteristics, like voters of the same party, in several districts. With their power of voting distributed, these groups fight to choose their preferred candidates in any of the districts,” as explained by the Brennan Center for Justice, a non-profit organization who defines itself as “an unbiased institution about politics and law.”
On the other hand, the people who define the maps “pack certain groups of voters in the smallest number of districts possible. In these few districts, it's likely that these packed groups chose their preferred candidates, but the power of voting of these groups will be debilitated in the rest,“ as this organization also mentions.
While this ill-intentioned process of redistricting affects all U.S. citizens, the Brennan Center, ally organization of Factchequeado, points that “the most significantly affected are the communities of color,” since the influence of their votes is limited.
According to the Brennan Center, “the residential segregation and the racial polarization of voting patterns, specially in the southern states, mean that putting the focus on the communities of color can be an effective tool in creating advantages for the party who controls the redistricting.”
Decisions of the Supreme Court
In the past years, the Supreme Court of Justice addressed different cases related to the manipulation behind the process of districting.
The 2017 sentence, Cooper v. Harris, denounced that there was gerrymandering in two districts in North Carolina, for which limits had been redefined after the 2010 census. This was considered illegal because it went against the Voting Rights Act, in which racial discrimination is forbidden.
Additionally, the resolution Rucho v. Common Cause and Lamone v. Benisek, signed in 2019, stated that claims that there is electoral manipulation are out of hands from the Federal Judicial power.
Instead, judges claimed that state and federal legislators are the ones who should apply laws so that there’s no manipulation in the process, and they decided it was not their responsibility to intervene in cases of gerrymandering.
Factchequeado is a verification media outlet built by a Spanish-speaking community to tackle disinformation in the United States. Do you want to be part of it? Join us and verify the content you receive by sending it to our WhatsApp +16468736087 or to factchequeado.com/whatsapp.
*Update: this article was updated on february 27th, 2024, before november 5th 2024 elections.